Sequential SSI components
Introduction
Unlike Combinational Circuits, most systems that one will encounter in practice will include Memory element thus being described in terms of sequential logic. The memory elements are devices capable of storing binary information within them. The binary information stored in the memory elements at a given time defines the state of the circuit. Thus a sequential circuit is specified by time sequence of inputs, outputs and internal states.
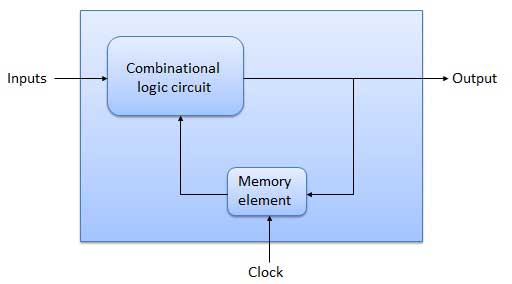
- This sequential circuit contains a set of inputs and output(s).
- The output(s) of sequential circuit depends not only on the combination of present inputs but also on the previous output(s).
- Previous output is nothing but the present state.
- Therefore, sequential circuits contain combinational circuits along with memory (storage) elements.
- Some sequential circuits may not contain combinational circuits, but only memory elements.
Following table shows the differences between combinational circuits and sequential circuits.
| Combinational Circuits | Sequential Circuits |
|---|---|
| Outputs depend only on present inputs. | Outputs depend on both present inputs and present state. |
| Feedback path is not present. | Feedback path is present. |
| Memory elements are not required. | Memory elements are required. |
| Clock signal is not required. | Clock signal is required. |
| Easy to design. | Difficult to design. |
Types of sequential circuits
Following are the two types of sequential circuits −
- Asynchronous sequential circuits
- Synchronous sequential circuits
Asynchronous sequential circuits
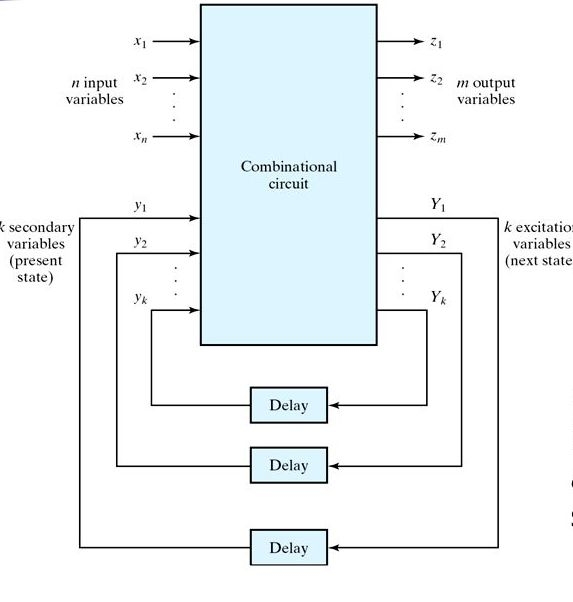
If some or all the outputs of a sequential circuit do not change (affect) with respect to active transition of clock signal, then that sequential circuit is called as Asynchronous sequential circuit. That means, all the outputs of asynchronous sequential circuits do not change (affect) at the same time. Therefore, most of the outputs of asynchronous sequential circuits are not in synchronous with either only positive edges or only negative edges of clock signal.
Synchronous sequential circuits
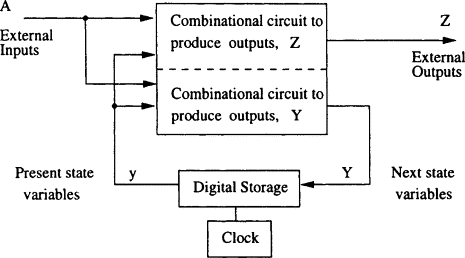
If all the outputs of a sequential circuit change (affect) with respect to active transition of clock signal, then that sequential circuit is called as Synchronous sequential circuit. That means, all the outputs of synchronous sequential circuits change (affect) at the same time. Therefore, the outputs of synchronous sequential circuits are in synchronous with either only positive edges or only negative edges of clock signal.
Chapter contents
- Basic level
- Clock signals
- Flip-flops
- Latches